There are 3 main types of variables:
- Local
- Parameter
- Instance
The scope of a variable is the part of the program where the variable can be accessed.
It’s good programming practice to keep the scope of all variables to a minimum.

Credit: this is a screen shot from slide nerd videos on youtube
The parameter variable val is available inside the orange box.
The local variable i is available inside the blue box
The local variable x is available in the purple box
2 local variables can have the same name providing their scopes don’t overlap.
E.g.
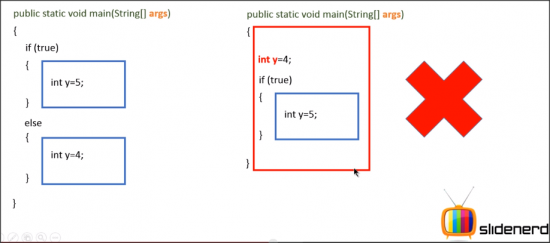
Credit: this is a screen shot from slidenerd videos on youtube
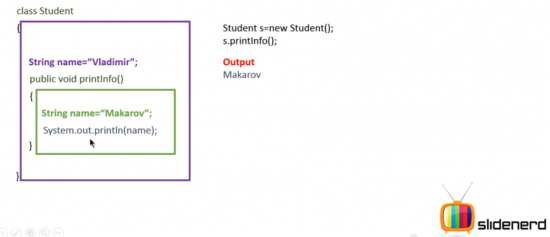
Instance variable scope

Credit: this is a screen shot from slidenerd videos on youtube
Instance variable shadowing
Credit: this is a screen shot from slidenerd videos on youtube
The above is fine as the purple is a instance variable, and the green is a local variable. You can always have local and instance variables with the same name. It’s only when you have 2 instance variables, or 2 local variables that they cannot have the same name.
In the following example:
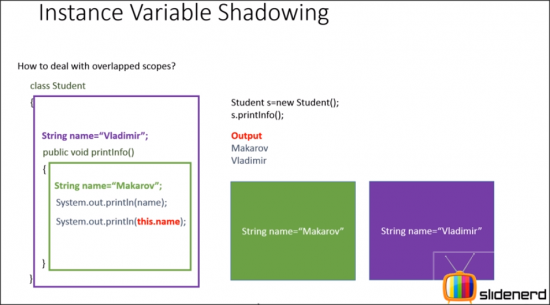
Credit: this is a screen shot from slidenerd videos on youtube
the first
System.out.println(name) will be Makarov, but the System.out.println(this.name) will be Vladimir
e.g.
public class ThisKeyword {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass myClass = new MyClass();
myClass.showInfo();
}
}
class MyClass
{
String name="James";
public void showInfo(){
String name="Froggy";
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
Outputs:
Froggy
James